Planning and selecting the right building materials are crucial for any construction project. This ensures durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness of the entire project. While several materials are used in construction projects, cinder and concrete blocks are essential. These two blocks stand out from other materials because of their versatility and strength. A layperson may get confused with these two blocks due to their similar appearances. However, they have different properties making them suitable for various applications. To make a better choice, understanding the differences, advantages, and limitations of the two blocks is essential. This article will be a perfect introductory guide on cinder blocks and concrete blocks, providing readers with a comprehensive view to choose the right material for their project.
What is a Cinder Block?
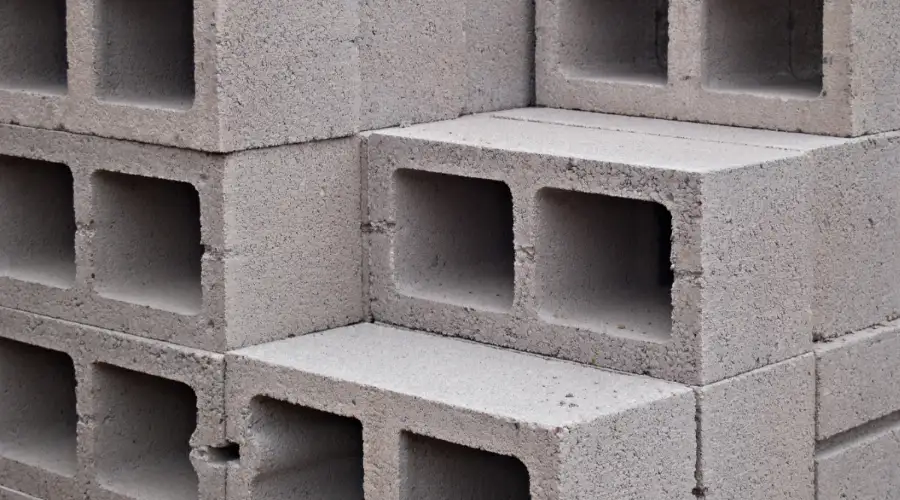

It is a lightweight building material made as a composition of cement, coal cinders, and water. Coal cinder are a by-product of coal combustion. Cinder blocks are light in weight and easy to handle as they are hollow in shape. Some of the common usages of cinder blocks are non-load-bearing walls, garden walls, and temporary structures. They are also known as concrete masonry units. The porous feature in cinder blocks leads to good insulation properties. This makes them suitable for specific climates and various applications.
What is a Concrete Block?
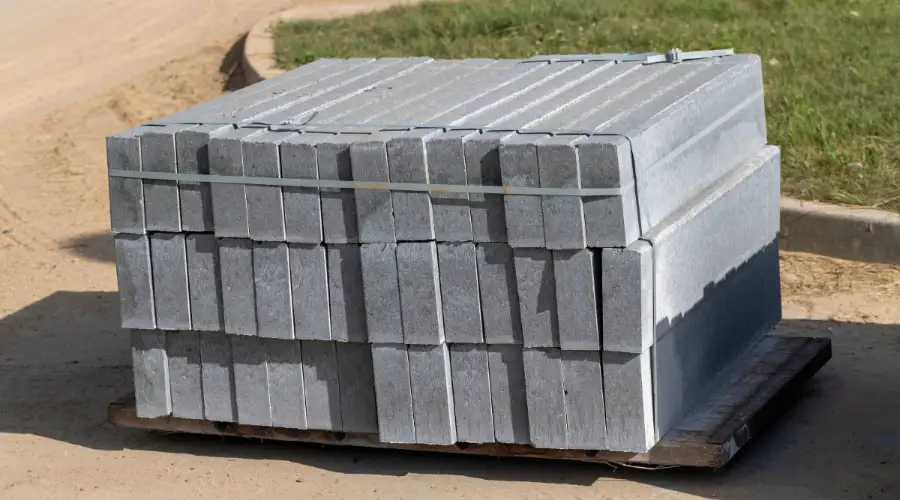

It is a robust and versatile construction material in comparison to cinder blocks. It is made up of cement, aggregate, and water. The aggregates, in this case, are sand or gravel. The absence of coal cinders provides concrete blocks with greater strength and density. Unlike cinder blocks, concrete blocks are available in both solid and hollow types. Some common applications of concrete blocks are load-bearing walls, foundations, and other structural applications.
Key Differences Between Cinder and Concrete Blocks
| Cinder Blocks | Concrete Blocks |
| The composition of cinder blocks includes cement, coal cinders, and water. | The composition of concrete blocks is cement, sand, gravel, and aggregates. |
| Its weaker strength and less durability make it suitable for non-load-bearing structures. | Concrete blocks are well-known for their strength and durability. This makes them ideal for structural and load-bearing applications. |
| The porous nature of cinder blocks reduces their weight drastically. | The dense composition of aggregates makes concrete blocks heavier than other solid blocks. |
| The air pockets in the block produce better insulation for the structure. | In comparison to cinder blocks, concrete blocks have lower insulation. |
| Cinder blocks are highly susceptible to weathering. | It can withstand weather, erosion, and moisture. |
| It is environmentally friendly as they use recycled materials like coal ash. | The use of cement and aggregates may increase the extent of damage to the environment. |
| It can be used in small places such as gardens or project walls. | It is used in all substantial construction projects. |
Advantages of Cinder Block
- Cinderblocks are light in weight. This makes them easy to handle.
- The low price of cinder blocks is suitable for small or temporary projects.
- The porous structure in cinder blocks extends insulation features.
Disadvantages of Cinder Block
- Its limited strength capability makes it unsuitable for load-bearing structures.
- It is highly susceptible to weathering and moisture damage.
- In most cases, cinder block structures require additional reinforcement.
Advantages of Concrete Block
- Its high compressive strength makes it suitable for structural applications.
- Unlike cinderblock, it is resistant to weathering and exposure to moisture.
- It requires low maintenance and is available in different shapes.
- Disadvantages of Concrete Block
- It requires additional effort during the installation process. This is because concrete blocks are heavier than cinder blocks.
- Compared to cinder blocks, they do not provide much insulation.
- Specialized tools for cutting and shaping are required.
Use Cases: When to Choose Cinder Vs Concrete Block
Both these blocks are used by constructors for a wide variety of purposes. The differences between cinder block and concrete block are very few; however, it is the type of project that determines the choice of preference. It is important to consider the facts about what you are building and what you expect as an outcome from that. Cinder blocks are ideal for lightweight and non-load-bearing projects such as garden projects or landscaping. In contrast, concrete blocks are best suited for load-bearing walls, foundations, and permanent structures such as retaining walls or steps.
Installation Process
Some of the basic steps that need to be remembered in the installation process of cinder and concrete blocks are,
- The construction site is cleared and levelled to the same height without any highs or lows.
- To ensure stability, lay a foundation on the cleared site.
- Here comes the placement of blocks. Blocks are bonded together with the use of mortar.
- Placement of blocks is important for the strength and stability of structures. Special care is required to align blocks leaving no gaps and maintain leveling.
- To increase the stability of the structure, additional supports such as steel bars or other reinforcement can be fixed.
- The constructed block structure should be left untouched for the mortar to cure and strengthen.
Maintenance and Longevity
Any structure’s sustainability depends on maintenance and care. Steps taken to ensure that the structure remains intact determine its longevity. Some measures to follow are
- Periodic inspection for the identification of cracks or damage is necessary. If discovered, immediate attention and repair are essential.
- Blocks should be sealed to prevent moisture absorption. This is specifically needed for cinder blocks.
- Regular cleaning of the surface with mild soap and water to remove dirt or stains on the structure will prevent any future damage.
- In the case of concrete blocks, longevity can be increased with repainting or re-sealing periodically.
Conclusion
The final decision for using cinder or concrete blocks is propelled by the requirements of each construction project. Cinder blocks are relatively cheaper and lighter when it comes to weight; however, they are not load-bearing components. On the other hand, concrete blocks exhibit strength and durability in robustness for building structures. Knowing their properties, scope of use, features, and shortcomings you can take necessary action and make very detailed decisions to maximise the positive outcome of the construction process to ensure that it is successful as well as to extend the timeframe of the building.
FAQs
In the construction sector, cinder blocks are not preferred for load-bearing applications because of their lower strength and structural integrity. In contrast, concrete blocks are recommended for such requirements.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, cinder blocks are more effective for non-load-bearing and decorative projects. However, in terms of durability and maintenance, over a period, cinder blocks’ cost may exceed concrete blocks’ cost.
Yes, they are still highly preferred by constructors for projects that demand setting up a garden wall, landscaping, and temporary structures. However, the introduction of many robust materials like concrete blocks has diminished the popularity cinder blocks once had.